Double Disc Couplings Clamping Type

Caution
Product Description
Disc Couplings are an economy item, The price is cheaper than the MISUMI standard product.They offer a wide variety of sizes to choose from.
[Feature]
● Shaft Hole Diameter Minimum/Maximum (mm.): 3 and 42
● Outside Diameter Minimum/Maximum (mm.): 12 and 82
● Overall Length Minimum/Maximum (mm.) : 19.5 and 98
● Material :
Hub - Aluminum Alloy
Disc - Stainless Steel
[Application]
Disc Couplings are commonly used in various applications in factory automation systems
Product Overview of Flexible Shaft Couplings
The Flexible Shaft Couplings relies on the elastic deformation of the disc to compensate for the relative displacement of the two shafts connected, is a high-performance flexible coupling with strong metal components.
It is characterized by compact structure, zero backlash, high strength, long service life, no rotating clearance, unaffected by temperature and oil, acid and alkali resistant and corrosion resistant.
Applicable motor types: Recommended for servo motors, stepper motors and general motors.
Dimensional Drawing of Flexible Shaft Couplings

Material table
| Type | Part |  Material Material |  Surface Treatment Surface Treatment |  Accessory Accessory |
| E-LMCPW | Hub | Aluminum Alloy | Clear Anodize | Hex Socket Clamp Screw |
| Disc | Stainless Steel | - |
Specification Table of Flexible Shaft Couplings
 ~
~  to select the part no. Please specify the shaft holediameter within the range of d1≤d2.
to select the part no. Please specify the shaft holediameter within the range of d1≤d2.Part No.( Type· Type· D) D) | - | 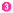 d1 d1 | - |  d2 d2 |
| E-LMCPW12 | - | 3 | - | 5 |
| E-LMCPW20 | - | 4 | - | 6 |
| Part No. | 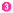 d1、 d1、 d2Shaft Hole Dia.(d1≤d2) d2Shaft Hole Dia.(d1≤d2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Type Type |  D D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E-LMCPW | 12 | *3 | *4 | *5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | *3 | *4 | *5 | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | *3 | *4 | *5 | 6 | 6.35 | 7 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | *3 | *4 | *5 | 6 | 6.35 | 7 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | *5 | 6 | 6.35 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9.525 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | *5 | 6 | 6.35 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9.525 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | *5 | 6 | 6.35 | 8 | 9 | 9.525 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.7 | 14 | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | *5 | 6 | 6.35 | 8 | 9 | 9.525 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.7 | 14 | 15 | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | *5 | 6 | 6.35 | 8 | 9 | 9.525 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.7 | 14 | 15 | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 39 | 8 | 9 | 9.525 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.7 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 44 | 8 | 9 | 9.525 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 12.7 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | ||||||||||||||||
| 56 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 32 | ||||||||||||||||
| 68 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 38 | |||||||||||||||
| 82 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 35 | 38 | 40 | 42 | |||||||||||||||||
| Part No. | L | F | Clam Screw | Tightening torque (N·m) | Allowable Axial Misalignment (mm) | Static Torsional Spring Constant (N·m/rad) | Maximum Rotational Speed (r/min) | Compensation Coefficient | Mass (g) | ||
| Type | D | M | Tightening torque N.m | ||||||||
| E-LMCPW | 12 | 15.9 | 2.2 | M1.6 | 0.23~0.28 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 133 | 10000 | 1 | 3.7 |
| 16 | 23 | 2.6 | M2 | 0.4~0.5 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 255 | 10000 | 1 | 10 | |
| 19 | 27 | 3.2 | M2.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.12 | 700 | 10000 | 1 | 14 | |
| 20 | 28.8 | 3.2 | M2.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.10 | 550 | 10000 | 1 | 19 | |
| 26 | 35 | 4 | M3 | 1.5 | 2 | 0.15 | 1850 | 10000 | 1 | 37 | |
| 29 | 34.3 | 4 | M3 | 1.5 | 2 | 0.15 | 1200 | 10000 | 1 | 43 | |
| 32 | 41 | 4 | M3 | 1.5 | 6 | 0.17 | 2850 | 10000 | 1 | 67 | |
| 33 | 40 | 4 | M3 | 1.5 | 6 | 0.20 | 1500 | 10000 | 1 | 60 | |
| 34 | 45 | 5 | M4 | 3.5 | 6 | 0.17 | 4050 | 10000 | 1 | 77 | |
| 39 | 50 | 5.2 | M4 | 3.5 | 13 | 0.22 | 9000 | 10000 | 1 | 118 | |
| 44 | 50 | 5.2 | M4 | 3.5 | 15 | 0.22 | 10000 | 10000 | 1 | 144 | |
| 56 | 64 | 6.3 | M5 | 8 | 28 | 0.27 | 25000 | 10000 | 1 | 318 | |
| 68 | 75 | 7.7 | M6 | 13 | 60 | 0.31 | 35000 | 9000 | 1 | 492 | |
| 82 | 98 | 9.8 | M8 | 28 | 100 | 0.55 | 70000 | 8000 | 1 | 1013 | |
Alterations of Flexible Shaft Couplings


| Shaft Hole Dia. d1 · d2 | b(Keyway Width) | t Keyway Depth | Keyway Nominal Dim. b X h | |
| LK | RK | |||
| 6 ~ 7.9 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2x2 |
| 8~10 | 3 | 3 | 1.4 | 3x3 |
| 11~12 | 4 | 4 | 1.8 | 4x4 |
| 13~17 | 5 | 5 | 2.3 | 5x5 |
| 18~22 | 6 | 6 | 2.8 | 6x6 |
| 23~30 | 8 | 8 | 3.3 | 8x7 |
| 31~38 | 10 | 10 | 3.3 | 10x8 |
| 39~44 | 12 | 12 | 3.3 | 12x8 |
Product Features of Flexible Shaft Couplings
1. Strong capability to compensate for misalignment of two shafts, offering twice the angular displacement compared to Jaw couplings, lower reactionary forces during radial displacement, high flexibility, and allows for certain axial,radial, and angular displacements.
2. Provides significant vibration damping effects, operates without noise, and wear-free.
3. Can safely operate under conditions of shock and vibration.
4. High transmission efficiency, up to 99.86%, particularly suitable for medium and high-speed, high-power transmission.
5. Simple structure, lightweight, small volume, and convenient for assembly and disassembly. Installation and removal can be done without moving the machine (refers to the type with an intermediate shaft) and does not require lubrication.
6. Can accurately transmit rotational speed, operates without slip, suitable for the transmission of precision machinery.
Example Use of Flexible Shaft Couplings

Precautions of Flexible Shaft Couplings
1. The coupling allows transmission of axis deviation, rotation angle and torque, but if the axis deviation exceeds the allowable value, vibration may occur or the lifespan will be drastically reduced. Please be sure to make corrections.
2. Axial deviation includes eccentricity (parallel error of two axes), declination (angular error of two axes), and axial amplitude (axial movement of the axes).
Perform calibration adjustment for the shaft so that the shaft center deviation is below the allowable value specified in the product dimensions and performance table.
3. The axial deviation tolerance values stated in the dimensions and performance tables refer to the situation when one of eccentricity, declination, and axial amplitude occurs individually. If two or moreaxial deviations occur simultaneously, the respective allowable values are reduced by half.
4. Axial deviation not only occurs when assembling the device, but is also a major cause of vibration, thermal expansion, and bearing wear during operation.
It is recommended that the axis deviation be set to less than 1/3 of the allowable value.